Add a library providing Olympe bricks as a npm dependency of a project
Once you have created a npm package providing Olympe bricks, you may want to add as dependency of another project in order to use that package bricks in that project. We will see how to do that and how to develop both the dependency package and the consumer project in parallel.
To follow this tutorial, you need first to create a new project using the Olympe Yeoman project-generator. In the process, your project dependencies are installed (with npm i). Here we assume that your project will be consumer of a package named string-utils that is globally available on your system as a npm package. If you don't know that already, you may want to learn how to build an Olympe project as a npm package and how to link a npm package you are currently developing to make it available on your system.
Add as dependency a package linked on the system
For Olympe tools to work correctly, the package.json of your project must specify that string-utils is amongst the project's dependencies.
If the package you want to use is already available on a distant npm registry, install it as usual with npm i string-utils from your project's root. Otherwise, add the dependency in your project package.json either by editing it manually or with npm pkg set dependencies.string-utils=<version> from your project's root.
Then, at your project's root, run
npm link string-utils
Details
Notes about packages linking
Any npm install or link operation will break existing links in your project. Thus, you must always- link all packages you want to link to your current project simultaneously, e.g.
npm link package1 package2 ... - relink all the packages after you have installed a new dependency with
npm i.
Finally, to formally add string-utils package as a dependency to your consumer project, run
npm run postadd
This operation will add the dependency in the source main src/main.js of your consumer project and reset the data cloud.
During this last operation, you'll be prompted to snapshot your data cloud before resetting it. It is highly recommended to perform a snapshot before resetting to avoid losing possible changes made in DRAW in your consumer project. Resetting is necessary to load the bricks of the imported package and make them available in DRAW. To make sure the bricks of the imported package are correctly loaded, check the reset logs: there should be a line stating that the package's bricks have been loaded:
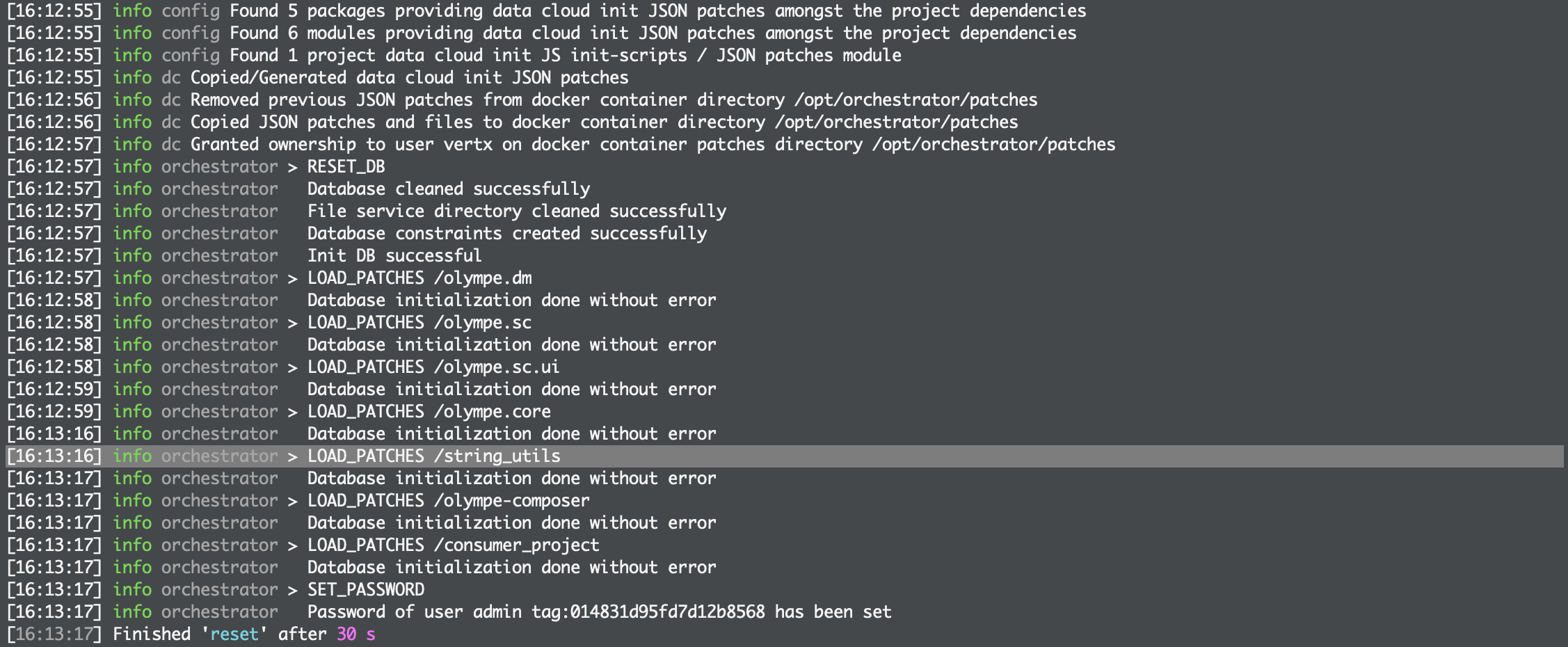
Once these operations are over, type as usual
npm run serve
which will serve DRAW on localhost:8888.
Use the bricks provided by the dependency package in the consumer project
When opening or reloading DRAW, you will see that both the library and the project are available on the data cloud. If not, try to reload the page.
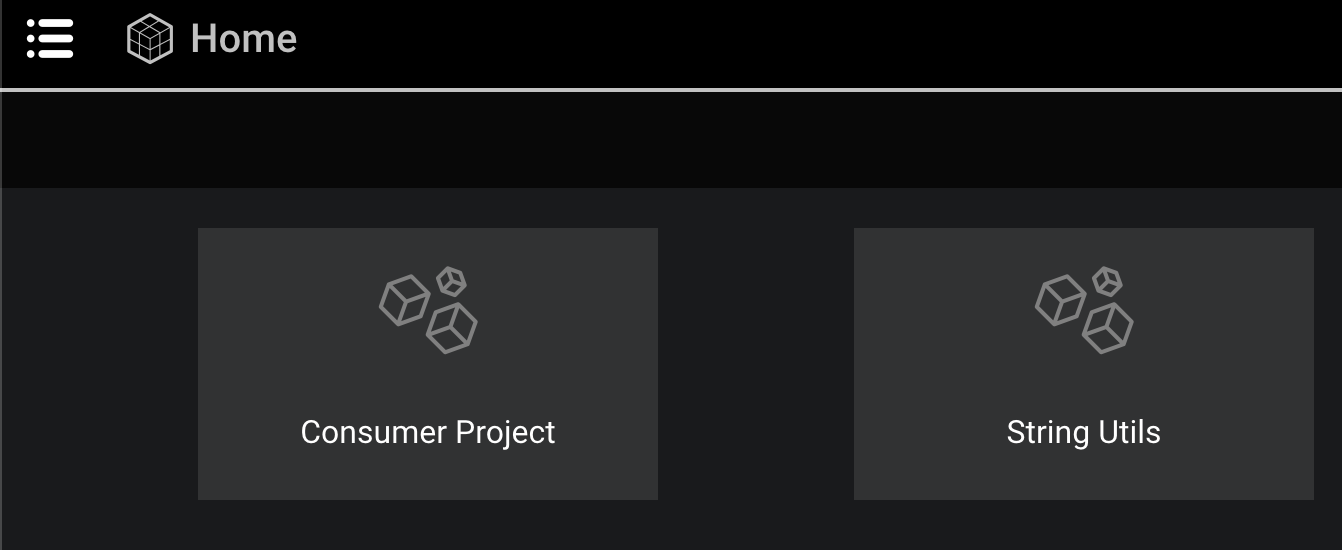
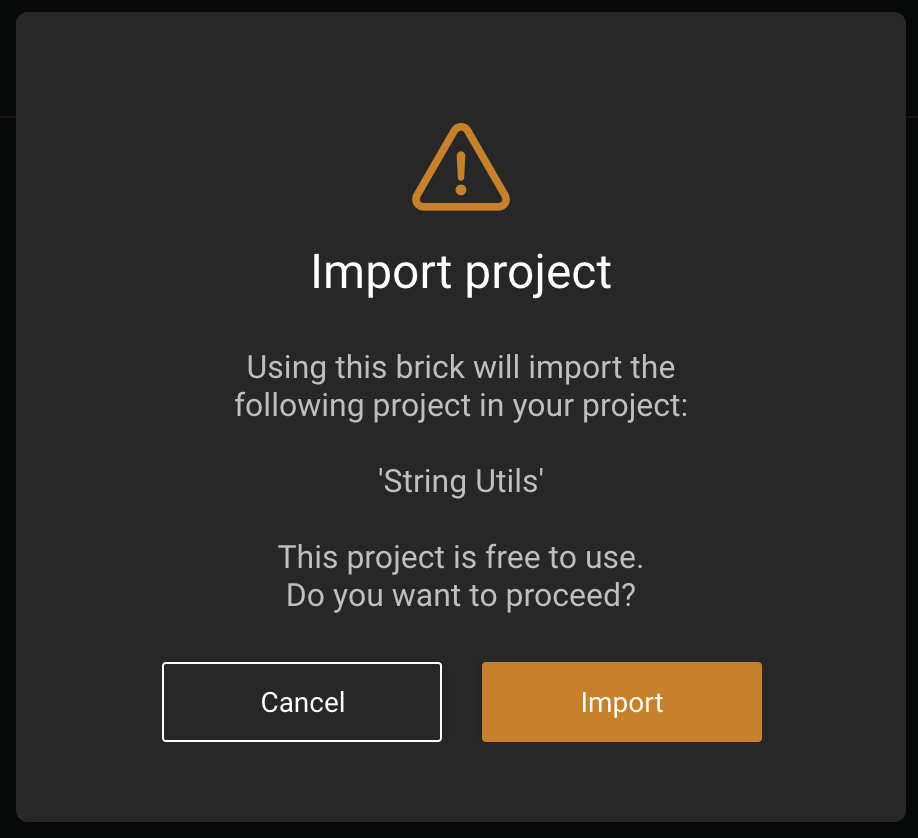
From now on, you can use in the consumer project function String Spacer provided by the dependency package. Note that the first time you want to use a brick provided by another package, you must look for it under the Community tab of the DRAW marketplace. Then, DRAW will ask you to confirm that you actually want to make that other package a dependency of your consumer project:
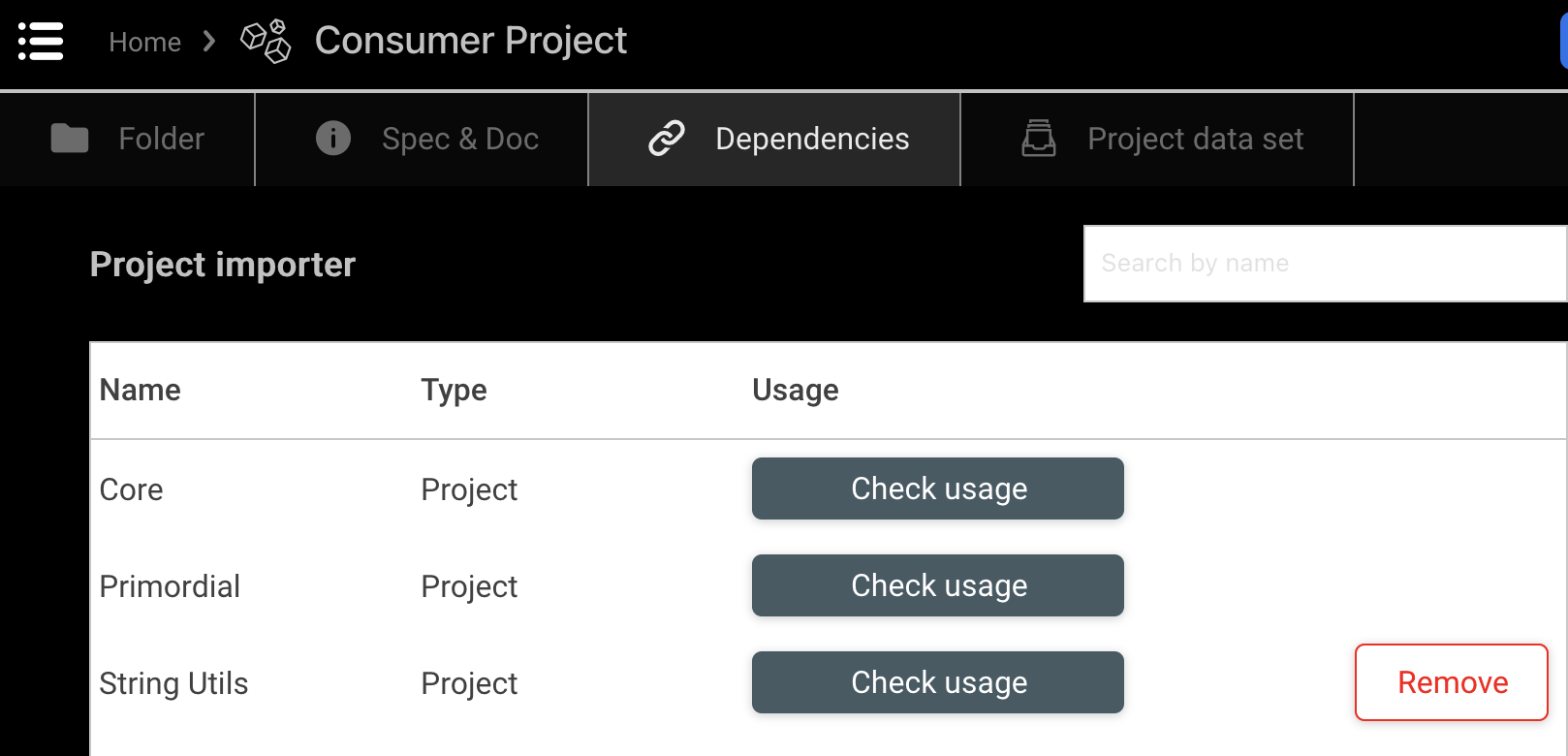
You can see the dependencies of your project in the Dependencies tab at the project's root in DRAW.
Work on both projects in parallel
It is possible to work on both the npm package and the consumer project in parallel. The requirement is to rebuild the package after every modification with command
npm run build
It is key to understand that even if you serve DRAW (with npm run serve command) from your consumer project, you can still modify String Utils project in DRAW. However, when you perform a npm run snapshot from your consumer project's root directory, you will only snapshot the consumer project's bricks. Any modification you bring in DRAW to the String Utils project must be snapshot from that project root directory.
Always think twice before resetting the data cloud, be it with npm run postadd or npm run reset command. Always make sure all your work is backed-up.